Govt issues new guidelines for home isolation of mild, asymptomatic COVID-19 cases
The Centre clarified that asymptomatic cases are those that are confirmed so by the laboratories but are not experiencing any symptoms and have oxygen saturation at room air of more than 94 %
The government has revised the guidelines for home isolation of mild and asymptomatic COVID-19 cases. These guidelines are in supersession of the guidelines issued on July 2, 2020.
As per the central guidelines, the patients who are clinically assigned to be mild /asymptomatic are recommended for home isolation.
Here are the revised guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare:
1. Asymptomatic cases; mild cases of COVID-19
The asymptomatic cases mean laboratory confirmed cases but not experiencing any symptoms and having oxygen saturation at room air of more than 94%.
Clinically assigned mild cases are patients with upper respiratory tract symptoms (&/or fever) without shortness of breath and having oxygen saturation at room air of more than 94%.
2. Patients eligible for home isolation
- The patient should be clinically assigned as mild/ asymptomatic case by the treating Medical
- Such cases should have the requisite facility at their residence for self-isolation and for quarantining the family contacts.
- A care giver should be available to provide care on 24 x7 basis. A communication link between the caregiver and hospital is a prerequisite for the entire duration of home
- Elderly patients aged more than 60 years and those with co-morbid conditions such as Hypertension, Diabetes, Heart disease, Chronic lung/liver/ kidney disease, Cerebro-vascular disease etc shall only be allowed home isolation after proper evaluation by the treating medical
- Patients suffering from immune compromised status (HIV, Transplant recipients, Cancer therapy ) are not recommended for home isolation and shall only be allowed home isolation after proper evaluation by the treating medical officer.
- The care giver and all close contacts of such cases should take Hydroxychloroquine prophylaxis as per protocol and as prescribed by the treating medical officer
- In addition, the guidelines on home-quarantine for other members available at: https://mohfw.gov.in/pdf/Guidelinesforhomequarantine.pdf, shall be also followed.
3. Instructions for the patient
- Patient must isolate himself from other household members, stay in the identified room and away from other people in home, especially elderlies and those with co-morbid conditions like hypertension, cardiovascular disease, renal disease etc.
- The patient should be kept in a well-ventilated room with cross ventilation and windows should be kept open to allow fresh air to come in.
- Patient should at all times use triple layer medical Discard mask after 8 hours of use or earlier if they become wet or visibly soiled. In the event of care giver entering the room, both care giver and patient may consider using N 95 mask.
- Mask should be discarded only after disinfecting it with 1% Sodium
- Patient must take rest and drink lot of fluids to maintain adequate
- Follow respiratory etiquettes at all
- Frequent hand washing with soap and water for at least 40 seconds or clean with alcohol-based
- Don’t share personal items with other people in the household.
- Ensure cleaning of surfaces in the room that are touched often (tabletops, doorknobs, handles, ) with 1% hypochlorite solution.
- Self-monitoring of blood oxygen saturation with a pulse oximeter is strongly
- The patient will self-monitor his/her health with daily temperature monitoring and report promptly if any deterioration of symptom as given below is noticed.
Monitoring chart
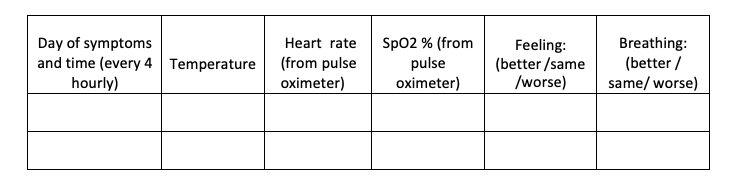
- Instructions for caregivers
i. Mask:
- The caregiver should wear a triple layer medical N95 mask may be considered when in the same room with the ill person.
- Front portion of the mask should not be touched or handled during
- If the mask gets wet or dirty with secretions, it must be changed
- Discard the mask after use and perform hand hygiene after disposal of the
- He/she should avoid touching own face, nose or
ii. Hand hygiene
- Hand hygiene must be ensured following contact with ill person or his immediate
- Hand hygiene should also be practiced before and after preparing food, before eating, after using the toilet, and whenever hands look
- Use soap and water for hand washing at least for 40 Alcohol-based hand rub can be used, if hands are not visibly soiled.
- After using soap and water, use of disposable paper towels to dry hands is If not available, use dedicated clean cloth towels and replace them when they become wet.
- Perform hand hygiene before and after removing
iii. Exposure to patient/patient’s environment
- Avoid direct contact with body fluids of the patient, particularly oral or respiratory Use disposable gloves while handling the patient.
- Avoid exposure to potentially contaminated items in his immediate environment (e.g. avoid sharing cigarettes, eating utensils, dishes, drinks, used towels or bed linen).
- Food must be provided to the patient in his Utensils and dishes used by the patient should be cleaned with soap/detergent and water wearing gloves. The utensils and dishes may be re-used.
- Clean hands after taking off gloves or handling used Use triple layer medical mask and disposable gloves while cleaning or handling surfaces, clothing or linen used by the patient.
- Perform hand hygiene before and after removing
iv. Biomedical Waste disposal
- Effective waste disposal shall be ensured so as to prevent further spread of infection within The waste (masks, disposable items, food packets etc.) should be disposed of as per CPCB guidelines (available at: http://cpcbenvis.nic.in/pdf/1595918059_mediaphoto2009.pdf)
5. Treatment for patients with mild /asymptomatic disease in home isolation
- Patients must be in communication with a treating physician and promptly report in case of any
- Continue the medications for other co-morbid illness after consulting the treating
- Patients to follow symptomatic management for fever, running nose and cough, as
- Patients may perform warm water gargles or take steam inhalation twice a
- If fever is not controlled with a maximum dose of Paracetamol 650mg four times a day, consult the treating doctor who may consider advising other drugs like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) (ex: Tab. Naproxen 250 mg twice a day).
- Consider Tab Ivermectin (200 mcg/kg once a day, to be taken empty stomach) for 3 to 5
- Inhalational Budesonide (given via inhalers with spacer at a dose of 800 mcg twice daily for 5 to 7 days) to be given if symptoms (fever and/or cough) are persistent beyond 5 days of disease
- The decision to administer Remdesivir or any other investigational therapy must be taken by a medical professional and administered only in a hospital setting. Do not attempt to procure or administer Remdesivir at home.
- Systemic oral steroids not indicated in mild disease. If symptoms persist beyond 7 days (persistent fever, worsening cough ) consult the treating doctor for treatment with low dose oral steroids.
- In case of falling oxygen saturation or shortness of breath, the person should require hospital admission and seek immediate consultation of their treating physician/surveillance
6. When to seek medical attention
Patient / Care giver will keep monitoring their health. Immediate medical attention must be sought if serious signs or symptoms develop. These could include-
- Difficulty in breathing,
- Dip in oxygen saturation (SpO2 < 94% on room air)
- Persistent pain/pressure in the chest,
- Mental confusion or inability to arouse,
7. When to discontinue home isolation
Patient under home isolation will stand discharged and end isolation after at least 10 days have passed from onset of symptoms (or from date of sampling for asymptomatic cases) and no fever for 3 days. There is no need for testing after the home isolation period is over.

Comments
Post a Comment